Timeline Index (Click Links Below to Skip to Specific Information)
|
(1852) It is discovered that corn can cross-fertilize in addition to self-fertilize. (1876) Charles Darwin: Cross- and Self-Fertilization in plants (left) (1879) William James Beal, an American botanist, makes the first controlled crossbreeds of hybrid corn in order to achieve higher yield. (right) |
|
 | (1953) Watson and
Crick discover the double helix structure of DNA. Knowing the structure of DNA
would then allow scientists to locate and “splice” out desired genes in the
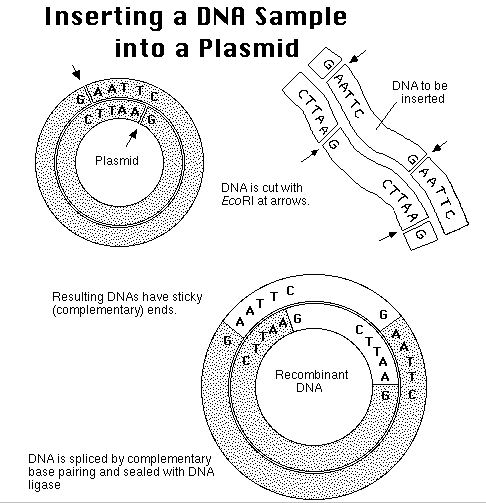
future. (below) (1972) Herbert Boyer
and Stanley Cohen develop a method of cloning desired genes in one organism and
transplanting the genes into another organism of a different species (recombinant DNA- left) This
discovery ushered in a new Era of genetic engineering. (Citations 18, 19)  |
(1980) In Diamond vs. Chakrabarty, the Supreme Court rules that genetically modified organisms could be patented. (1982) The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves the first genetically engineered drug, Humulin, human insulin produced by transformed bacteria. This innovation revolutionized diabetes treatment because less effective and harder to collect animal insulin was no longer needed. (1986) US and French scientists create the first transgenic crop: tobacco plants with herbicide resistance.(right) (Citation 20) |  |
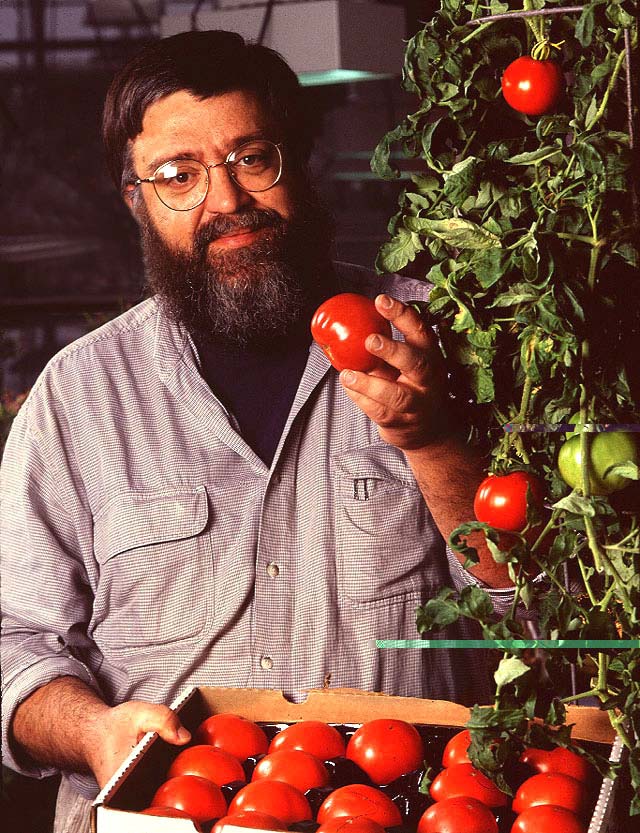 |
(1990) The USA conducts the first successful field trial for
herbicide resistant cotton. (1998) South Africa authorizes the first genetically modified crops for disease and drought tolerance. (Citations 21,22,23,24) (Left- USDA plant physiologist examining GM tomatoes engineered to ensure longer shelf life)
|
(2003) 180 countries ratify the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity, an international agreement aimed at monitoring the safety of living modified organisms (LMOs)(2008) A group of genes that increase rice yield during drought conditions is discovered. (right) (Citation 25) |  |
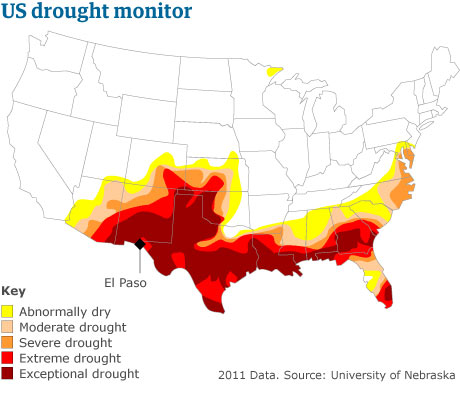 |
(2010) Controlled field trials for GM maize sponsored by the African Agricultural Technology Foundation (AATF) begins in Kenya and Uganda. (2011) Bangladesh Rice Research Institute (BRRI) introduces three new rice varieties with drought, cold and salinity resistance.
(2012) Monsanto Co.
plans a large-scale test of the first US government approved GM crop with
drought-tolerance in order to serve Southern states facing unusual drought
conditions. (Citation 26) |